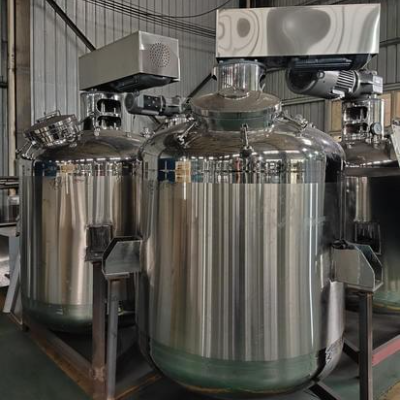
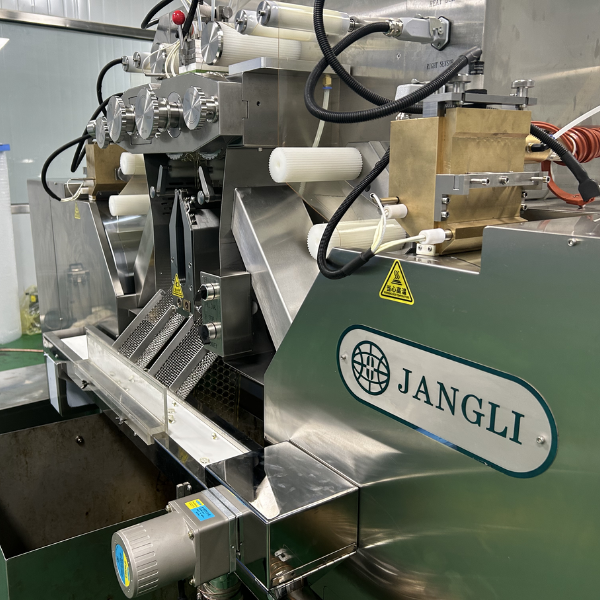
Gelatin is the main component in making soft gel capsules. Its preparation is critical as it determines the quality of your capsules. Gelatin creates the outer shell for soft gel capsules. Hard capsules are commonly filled with granules, pellets, mini-tablets, and powders. On the other hand, soft gel capsule fillings are either liquid or semi-solid.
Soft capsules are hermetically sealed one-piece flexible shells. The gelatin shell readily dissolves in gastric juices in case of pharmaceutical use. Soft gel encapsulation machines efficiently encapsulate liquid and semi-liquid materials within a gelatin shell.
In this article, I discuss the role of gelatin in soft gel encapsulation machines, the process of preparing and melting gelatin, the factors influencing gelatin mixing, and its properties. Finally, I explain the different types of gelatins and their suitability for soft gel encapsulation.
The Role of Gelatin in Soft Gel Encapsulation Machines
Choosing the right gelatin ensures that the soft gel encapsulation process is smooth and efficient. When you choose a gelatin mass with consistent formulation performance and minimal foaming, you lower your production costs due to decreased defects. You’ll have better output from your soft gel encapsulation machine by understanding different gelatin types, foaming capabilities, and stability.
Gelatin has essential functions in soft gel encapsulation machines.
- Shell formation: Gelatin forms the outer shell of the soft gel capsule. When the gelatin in the melting tank melts, it flows into the capsule die roller cavities. Gelatin solidifies upon cooling, creating a solid shell enclosing the fill material.
- Compatibility: Gelatin is compatible with various fill-in materials such as powders, pastes, oils, and suspensions. It can encapsulate both water-loving and water-resistant substances. Hence, making it suitable for encapsulating different types of active ingredients and formulations.
- Elasticity: Soft gel capsules are known for their ability to withstand mechanical stress without breaking or leaking. Gelatin’s elastic nature contributes to soft gel’s ability to accommodate different fill materials while maintaining its shape during handling, transportation, and usage.
- Encapsulation integrity: Gelatin acts as a barrier and effectively encloses while protecting the fill material from external contaminants, light, oxygen, and moisture. So that it ensures the integrity and stability of the encapsulated product, gelatin provides a stable and reliable encapsulation system.
- Solubility: Since the gelatin shell is readily soluble in the digestive system, it allows for efficient release and absorption of the encapsulated fill material in the body.
- Viscosity: The viscosity of gelatin ensures uniform coating of the fill-in materials, forming smooth and visually appealing soft gel capsules. Viscosity in gelatin helps in ribbon forming. Finding the proper viscoelastic gelation behavior can create the perfect ribbon for soft gel capsules, ensuring production efficiency. The soft gel machines will form poor films when the gelatin you want to use has low-quality viscosity properties. It also slows down the speed of the ribbon setting.
Various gelatin properties significantly impact the quality and performance of soft gel capsules. High gel strength is necessary for soft gel encapsulation machines to reduce the risk of shell breakage or leakage.
Hence, gelatin’s role in soft gel encapsulation machines is crucial for creating high-quality, easy-to-swallow soft gel capsules.
Read our article on equipping your soft gel production line for success.
What Is the Process of Preparing and Melting Gelatin?
The preparation of gelatin is a critical step in producing high-quality soft gel capsules. The melting process of gelatin involves transforming solid gelatin into a molten form by applying heat. It is crucial for the successful formation of the soft gel capsule. You can undertake the following steps to prepare and melt the gelatin.
- Begin by selecting high-quality gelatin that meets the specific requirements of the soft gel encapsulation process. Gelatin varies in viscosity, bloom strength, and other properties. Ensure you get gelatin with high-quality grade and bloom strength to avoid soft gel defects. Your soft gel encapsulation machine will also risk damage if you use poor-quality gelatin.
- Weigh the required amount of gelatin powder. Add the gelatin to a suitable solvent. The most common being water or a mixture of water and glycerin. Calculate the ratio of gelatin based on the desired viscosity and concentration of the solution.
- Transfer the gelatin solution to a melting tank with temperature controls and agitation mechanisms.
- Mix gelatin and the solvent thoroughly to allow the mixture to spread quickly. You can use gentle heating to aid in the dissolution of gelatin. Melting temperatures for gelatin usually range from 95-113°F (35-45°C), though it also depends on the gelatin grade and the intended application. But avoid excessive heat that can degrade the gelatin properties.
- Stirring and agitation during heating promote uniform mixing, achieving a homogenous solution. Agitation helps to distribute the heat uniformly, promoting the dissolution of the gelatin.
- The next step is conditioning and aging the gelatin. Conditioning allows the gelatin solution to rest for a specified period to allow air bubbles or foam to dissipate. Aging the gelation solution for a certain period, on the other hand, enhances its gelling properties contributing to the overall quality of the soft gel capsules.
- Purify the gelation solution to remove impurities or undissolved particles before transferring it. Doing so protects your soft gel encapsulation machine from damage, and you’re assured of getting high-quality capsules. You can use filter paper or specialized filtration systems.
- Pump the gelatin into the soft gel encapsulation machine’s gelatin tank once it has melted. When gelatin reaches its melting point, it becomes a viscous liquid state. The melted gelatin is ready for further processing, such as encapsulation, coating, or molding.
It’s important to note that gelatin should be compatible with the specific fill materials that you will use in the soft gel capsules. Hence, it should not react chemically or affect the fill-in materials.
What Factors Influence Gelatin Melting?
A few factors can influence the melting process to get to that excellent molten gelatin. Considering the following factors, you’ll get a smooth and consistent molten gelatin for your soft gel encapsulation process.
Moisture content and hydration
Gelatin have a high affinity for water and the presence of water aids in its melting process. Excessive moisture, however, will affect its properties, and too little moisture hinders the melting process.
You can pre-hydrate the gelatin in water before melting to ensure uniform moisture distribution to facilitate the melting process.
Temperature and time parameters
Because heating is necessary when melting gelatin, the right temperature is vital. The specific type and grade of gelatin you’re using dictates the temperature. The time it takes for the gelatin to melt also depends on the type and grade of gelatin.
Ensure that the temperature you’re working with melts the gelatin smoothly without overheating or degrading its properties. Do the melting gradually to ensure thorough melting and prevent any hot spots.
Techniques and equipment
You can use various methods to melt your gelation. Hot water baths, steam-jacketed vessels, and specialized gelatin melters are the most common. However, the soft gel encapsulation machine has a melting tank to melt the gelatin.
What Are the Properties of Gelatin?
Gelatin comes from animal sources such as porcine collagen, fish, and bovine. Its many properties and characteristics make it popular in various industries, such as food, paint, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. Understanding these properties helps in exploiting gelatin’s potential in various industries.
- Gelatin’s low melting and boiling points give it superior mechanical resistance and seal quality. Its ability to melt at body temperature makes it ideal for pharma capsules, gummies, water jellies, gelatin desserts, and marshmallows.
- Its ability to form a gel and mix well with other ingredients is due to amino acids (glycine, proline, hydroxyproline).
- Gelatin is soluble in acetic acid, glycerol, and hot water. It is insoluble in most organic solvents such as acetone, benzene, ether, alcohol, chloroform, and oils.
- It has higher bloom strength (a measure of gelatin’s gelling ability) which is ideal where gel strength is necessary, such as soft gel encapsulation.
- Gelatin falls in the category of clean labels as it doesn’t require a lot of processing. It contains neither preservatives, uric acid compounds, cholesterol, nor other additives. By being biodegradable, gelatin is ideal for medical, food, and pharmaceutical applications.
- As a molecular structure, gelatin has three polypeptide chains that form a collagen-like structure. The structure increases gelatin’s gelling and binding properties.
- Gelatin is a colorless, brittle, nearly tasteless, translucent solid substance. It is a hydrolyzed form of collagen. Its color is white to slightly yellow powder. Gelatin exists in various forms, such as powder, granules, and sheets.
The above properties ensure proper gelatin flow, mold release, and consistent soft gel capsule formation.
Different Types of Gelatin and Their Suitability for Soft Gel Encapsulation
There are various types of gelatin. Each type has its own set of characteristics and suitability for soft gel encapsulation. Choosing a particular gelatin type will depend on several factors, such as the processing requirement, the fill materials, and the desired characteristics of the final soft gel product.
Below is a table showing different types of gelatins and their characteristics.
| Types of Gelatin | Characteristics |
| Type A gelatin | -Derived from hydrogen hydrolysis of collagen. |
| -Preferred in applications that require lower viscosity. | |
| -For soft gel encapsulation machines, its quick gelling characteristics make it the best choice. | |
| -Ideal for delicacies like jellies, sauces, delectable delights, and other food-grade products. | |
| Type B gelatin | -Derived from alkaline hydrolysis of collagen. |
| -Compared to Type A gelatin, it exhibits different gelling properties. | |
| -Mainly used for industrial purposes. | |
| -Low bloom strength. | |
| -Higher viscosity. | |
| Fish gelatin | -For those with dietary restrictions or religious considerations, fish gelatin provides an option. |
| -Extracted with hot water from collagen-rich fish skin/scale material. | |
| -Limited range of applications. | |
| -It can still be used in soft gel encapsulation if it satisfies the necessary quality standards and is compatible with the fill material | |
| -Light yellow. | |
| –A nutritious natural source of pure protein. | |
| Pharmaceutical grade gelatin | -Has a higher bloom strength and viscosity. |
| -Derived from skins and bones of animals through partial hydrolysis. | |
| -Is put through stringent controls to ensure it’s pure and compatible with the fill materials. | |
| -Makes film-coated pills, hard and soft capsules, and more. | |
| Low endotoxin gelatin | –Essential in pharmaceutical soft gel encapsulation where rigorous quality and safety criteria must be met. |
| -Multiple uses in the development of medical devices, regenerative medicine, and tissue engineering research | |
| -Extracted from alkaline-treated pig skin | |
| -Endotoxins are naturally occurring chemicals present in the cell walls of bacteria. They may be harmful when present in pharmaceutical products. |
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between gelatin and cellulose capsules?
Animal-sourced gelatin is used to make gelatin capsules. A plant-based polymer obtained from vegetable sources, cellulose is the main component of cellulose capsules.
Various substances, including vitamins, dietary supplements, herbal extracts, and medications, are encapsulated in gelatin capsules. Plant-based or vegetarian medications are frequently enclosed in cellulose capsules.
- Why are plasticizers important in capsule shells?
Plasticizers make gelatin more flexible and shield the capsules from damage during handling, transportation, and use. They aid in preserving the capsule shell’s flexibility, enabling it to receive the fill ingredients without changing shape.
The ability of the capsule to pass through the throat easily is improved by the plasticizers used in the shell creation of the capsule, lowering the possibility of choking or discomfort. They also ensure that the produced capsules are released smoothly and efficiently from the molds used to fill them with the gelatin solution.
They aid in the shell’s ability to effectively seal off the encapsulated fill material to avoid leakage or evaporation. The capsule shell is flexible due to the plasticizers present, enabling a secure and tight seal between the two sections of the capsule.
For soft gel encapsulation, sorbitol liquid, glycerine, polyethylene glycol (PEG), and propylene glycol are the most popular plasticizers. Choose plasticizers that work well with the fill substance and gelatin. The plasticizers shouldn’t impact the stability or quality of the fill material.
Conclusion
If you want to manufacture high-quality soft gel capsules, you need to understand the function of gelatin in soft gel encapsulation machines. The primary component used to create the capsules’ exterior shell is gelatin.
You need not worry about the equipment that you will need for encapsulation. We at Jangli Equipment are prepared to assist you with your equipment needs throughout the soft gel encapsulation process.