Softgel capsules refer to sealed capsule preparations formed by quantitatively packing oily medicine, medicine solutions or suspensions using gelatin as the main material of the capsule shell. Common preparation methods include dripping and encapsulation. This article briefly describes the preparation process and precautions of the soft capsule encapsulation method.
Basic Principle of Softgel Encapsulation Process
The gelatin film(formed ahead from spreader boxes and casting drums) passes through the middle of a pair of cylindrical molds(die rollers), the medicine feeding pump injects a certain amount of medicine liquid into the gelatin film through the injection segment, and the molds(die roller) move toward each other to press the two pieces of gelatin film and cut them out from the gelatin to form completely closed capsules.
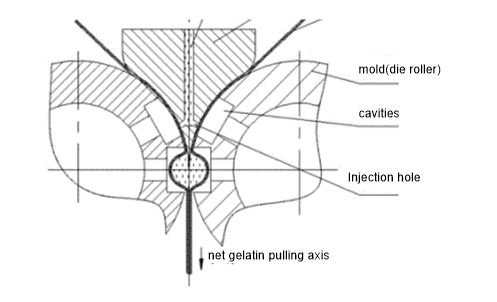
Softgel Manufacturing Process
- Gelatin Melting
- Medicine Liquid Mixing And Preparation
- Softgel Encapsulation
- Softgel Drying
- Softgel Inspection and Sorting
Gelatin Melting
- Material feeding sequence
Usually, a certain proportion of gelatin, plasticizer and water is added to the gelatin melting tank, heated and stirred, and the gelatin absorbs water and melts to form a gelatin liquid. The above materials can be put in at the same time, but it is recommended not to put gelatin directly into hot water. Otherwise, after the part of gelatin that comes into contact with hot water first, a dense gelatin layer will be formed, and the gelatin particles wrapped inside will be difficult to dissolve, and there will be some residue in the obtained glue. There are many clumps, which affects normal production. In addition, pigments or opacifying agents, such as titanium dioxide, iron oxide, etc., may be added to the gelatin. Use a colloid mill to grind it together with some plasticizers and water, and then add it to the gelatin after sieving to avoid pitting or pores in the prepared gelatin film.
- Temperature control
The temperature of gelatin solution in production is generally controlled at 60~70℃. The main component of gelatin is a mixture of polypeptide molecules. Excessive temperature will cause hydrolysis of the polypeptide molecules and affect the quality of the final gelatin liquid.
- Vacuuming and debugging
There will be many bubbles in the newly melted gelatin, so vacuum degassing is required. Generally, the vacuum degree of vacuum degassing should reach -0.07~-0.08MPa. At the beginning, a large number of bubbles will be rolled and released from the gelatin liquid. Therefore, be careful to relieve the pressure in time to avoid pumping the glue into the vacuum pump and damaging the equipment. During the vacuuming process, pay attention to the state of the gelatin until no obvious bubbles are released on the surface and the gelatin surface flows in a honeycomb shape, indicating that degassing is complete and the vacuuming operation can be stopped. The vacuuming time should not be too long, otherwise the gelatin will lose a lot of water, which will affect the subsequent softgel encapsulation operation.
- Gelatin solution insulation
After melting, the gelatin liquid should be transferred to gelatin service tanks for insulation. The insulation temperature of the gelatin solution is generally controlled between 50 and 60°C. If the temperature of the gelatin solution is too low, the fluidity will become poor, and the gelatin solution still needs to be reheated during the softgel making stage, which takes a long time and Thegelatin properties may be uneven.
The gelatin should not be used immediately after vacuum degassing is completed. It needs to be left for more than 4 hours to allow the bubbles in the gelatin to be fully discharged. The upper limit of the insulation time is inspected according to the specific project. The viscosity, freezing force and moisture of the gelatin during the insulation process can be monitored to determine the insulation process.
Medicine Liquid Mixing & Preparation
The filling contents can be prepared according to the requirements of specific softgel making projects, and the liquid preparation process can be controlled with reference to the relevant technical requirements for solutions, suspensions, and semi-solid preparations. If the raw materials are unstable to light, heat, or oxygen, consider avoiding light, cooling, or filling with nitrogen. The medicine preparation process varies depending on the specific project, so it will not be discussed in detail here.
Softgel Encapsulation
Softgel encapsulation is the core work of soft capsule production. Add the configured medicinal liquid into the hopper, and send the gelatin liquid to the soft capsule machine through the hose to complete the gelatin film preparation, quantitative filling of the content, and the gelatin and content through the die roller and made into capsules. The main process parameters that need to be controlled are as follows:
- Gelatin film thickness
If it is a generic preparation, the thickness of the soft capsule shell is recommended to be consistent with that of the reference preparation to ensure consistent disintegration time. Wet gelatin film of different thicknesses can be laid with a determined prescription. After drying, the thickness of the dry shell is measured to determine the target gelatin film thickness range. Under normal circumstances, the thickness of gelatin film with a weight of 1g and above is controlled at 0.8~0.9mm, and the thickness of gelatin ribbon with a weight of less than 1g is controlled at 0.7~0.8mm. If the gelatin ribbon is too thick, the required temperature of the die roller wedge may be higher, otherwise the stitching effect will not be good. If the gelatin ribbon is too thin, it will affect the pressure resistance of the soft capsule and is not conducive to storage and transportation. In addition, the thickness of the two pieces of gelatin film should be as consistent as possible, otherwise deformed softgels will be produced.
- Temperature of die roller segment
The temperature of the die roller segment is adjusted according to the condition of the gelatin film. If the moisture content of the gelatin film is too low or the gelatin ribbon is too thick, the temperature of the segment should be increased appropriately. In addition, if the injecting speed is too high, the temperature of the wedge also needs to be increased to ensure a better sealing effect. Generally, the temperature of the segment should be controlled at 35°C to 40°C. If it is too low, it will be difficult to seal. If it is too high, the sealing line of the soft capsule may be distorted and abnormal capsules may be produced.
- Softgel die roller rotating speed
The increase in the speed of the rotating speed may not only affect the temperature of the segment, but may also affect the thickness of the gelatin ribbon. A faster rotational speed will overstretch the gelatin film during the softgel encapsulation process, causing the gelatin film to become thinner. Therefore, after adjusting the die roller rotating speed, the gelatin film thickness should be monitored to ensure that the gelatin ribbon thickness is within the target range.
- Environment temperature
The ambient temperature during the softgel capsule encapsulation process will also affect the encapsulation effect. If the ambient temperature is too high, it may cause the capsules to cool slowly and cause adhesion. If the ambient temperature is too low, the gelatin film will be difficult to seal, and the temperature of the segment needs to be increased appropriately.
- Others
During the soft gelatin capsule making process, it is also necessary to control the temperature of the gelatin transferring pipe, the temperature of the gelatin spreader boxes, the temperature of the casting drums, etc. The temperature of the gelatin transferring pipe and the gelatin spreader boxes are generally 55~60℃ to ensure that the gelatin solution can flow smoothly without causing blockage of the gelatin transferring pipe; the casting drum is generally controlled below 20℃ to ensure that the gelatin film can be quickly cooled and formed.
In addition, during the soft capsule making process, attention should also be paid to the type and amount of lubricating oil added, and corresponding quality standards should be formulated for the lubricating oil. There should be sufficient evidence to prove that the lubricating oil will not affect other components of the soft capsule. Commonly used lubricants include pharmaceutical grade liquid paraffin and medium chain glyceryl esters.
Softgel Drying
The softgel drying process is generally divided into two steps, namely setting drying and standing drying. Shaping drying means that the freshly encapsulated soft capsules are immediately transferred to a drying basket for drying, so that the moisture content is reduced to 25~30%. At this moisture content, the shape of the soft capsules is basically finalized. In order to improve production efficiency, the shaped and dried soft capsules are transferred to a tray to continue drying. In order to clean the lubricating oil on the surface of the soft capsule, an oil-absorbing cloth can be added to the drying cage during the drying process.
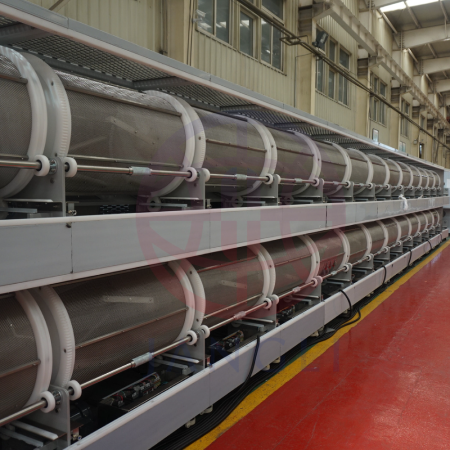

ALT: double deck softgel drying tumble dryer

ALT: softgel oil absorbing cloth
Generally, the moisture content of soft capsule shells should be controlled between 8 and 12%. If the moisture content is too high, the finished capsule shell will be too soft and prone to mold; if the moisture content is too low, the capsule shell will become brittle, which is not conducive to storage and transportation. The factors that affect the drying effect of soft capsules mainly include the following three points:
- Ambient temperature and humidity
Research by someones shows that the effect of changes in drying conditions on the drying rate of soft capsules is shown in the following figure. The temperature of the drying environment is high, and the soft capsules dry faster in the early stage of drying. However, in the later stage of drying, due to drying and hardening of the capsule shell surface , affecting the internal moisture conduction, and the drying rate decreases. As the ambient humidity decreases, the drying rate shows an accelerated trend. Under normal circumstances, the ambient humidity should be controlled below 60%, otherwise the capsules will be extremely difficult to dry.
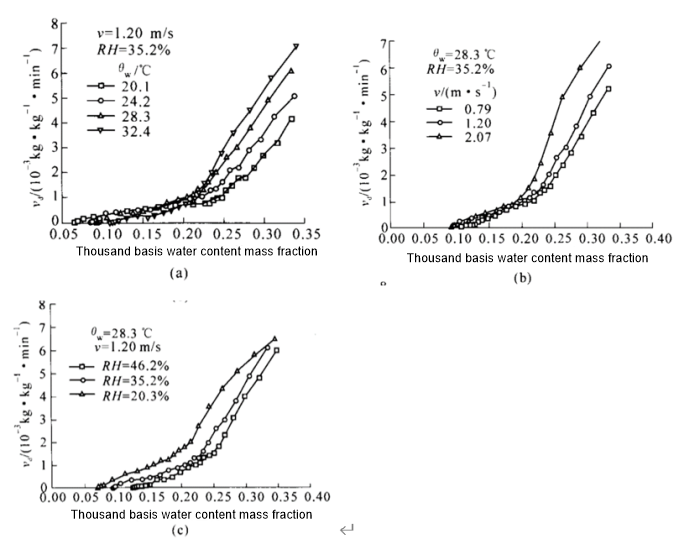
- Drying air speed
Increasing the wind speed in a dry environment can increase the moisture transfer rate and improve drying efficiency.
- Drying time
Under strict control of ambient temperature and humidity, the moisture content of dry soft capsules depends on the length of drying time. During the process inspection stage, capsules with different drying times can be taken to measure the capsule shell moisture and a drying curve can be drawn to determine the drying end point.
Softgel Inspection and Sorting
The soft capsule inspection process is to eliminate unqualified products in dry soft capsules, such as large and small capsules, flat capsules, bubble capsules, special-shaped capsules, etc. The general method of capsule inspection is to place the soft capsules on a light inspection table and select them manually. There is also automatic softgel inspection and sorting equipment available now, and this equipment can detect and kick out the soft capsules with bad shapes, sizes or colors automatically.
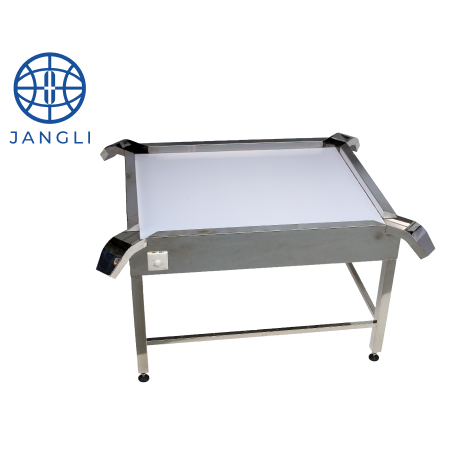

ALT: manual softgel light inspection table
Precautions During Softgel Production Process
In the soft capsule preparation process, we need to evaluate the output material properties of each process to ensure the output of qualified products.
In the gelatin melting stage, the appearance, moisture, viscosity, and freezing force of the gelatin are generally used as inspection indicators. The appearance of the gelatin solution should be delicate and smooth without fine bubbles; the moisture should be controlled at 40%-50%. If the moisture is too low, it will be difficult to sealing during the softgel making process. If the moisture is too high, it will be difficult to form the a ribbon; the viscosity and freezing force are of the quality of gelatin. The main testing indicators are: if the viscosity is too low, the soft capsule shell is easy to saponify. These two indicators should be monitored during the gelatin insulation process to prevent the quality of the gelatin from declining too much.
In the capsule encapsulation stage, the main indicators of concern are the appearance, filling volume and sealing condition of the soft capsule. The appearance focuses on whether there are bubbles on the surface of the capsule and whether the seams are smooth. To measure the filling volume, the soft capsule needs to be cut open, and the weight of the capsule shell is measured after wiping off the contents. There are also preparation quality standards that recommend the use of ether to clean the contents. The filling capacity is the difference between the total weight of the capsule and the weight of the capsule skin. It should be measured immediately after the sample is taken out. If the waiting time is long, the evaporation of the water in the soft capsule will affect the accuracy of the filling capacity measurement result; if it cannot be measured immediately, soft capsules need to be stored in an airtight container and placed in a low-temperature environment to prevent moisture from evaporating; the suture condition can be observed with a microscope. The measurement method is to cross-cut the newly prepared soft capsule, cut off a circle of gelatin shell in the middle, and observe the gelatin skin under a microscope. The thickness and the thickness of the seam, measure and calculate the seam rate, generally the seam rate should not be less than 30%.
Capsule seam rate = seam thickness/shell thickness*100%
Recommend this Softgel Seam Inspection Equipment to you

ALT:the microscope mirror image of a gelatin shell cross-section
During the softgel drying stage, attention should be paid to monitoring the moisture content of the capsule shell. The measurement method is to cut the soft capsule, dry the contents in the capsule shell with oil-absorbing paper, and measure the moisture content of the capsule shell using the drying method, and this softgel moisture content tester is good choice. Generally, the measurement is performed once every 8 to 12 hours until the moisture content is reached. Reach the target range. If there is a proven method for monitoring moisture reliably, this may be used.

